

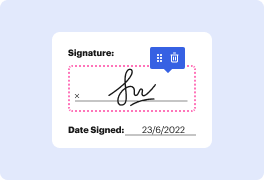

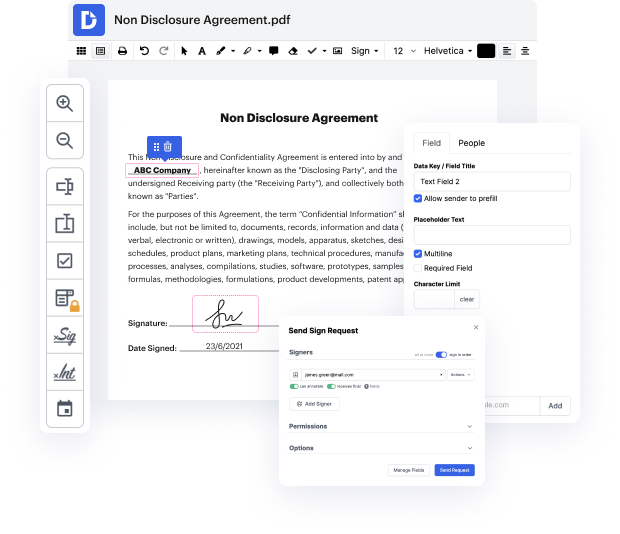
DocHub provides an efficient way to manage your documents online, allowing you to edit, sign, and distribute files seamlessly. With its robust integration with Google Workspace, our platform simplifies the process of importing, exporting, and modifying documents directly from Google apps. Whether you're using iOS 17, iOS 18, or iOS 19, DocHub ensures a smooth experience for all users. This guide will walk you through how to remove data documents in Linux, leveraging our editor’s powerful features.
Start using DocHub today to streamline your document management process and enjoy effortless editing and signing online for free!
if youve been using windows the mac os or even a linux distro that is designed similarly to one of them youve probably tried deleting a file by dragging it into the recycle bin or pressing delete on the file to place it there and then emptying out the recycle bin but this method of file deletion doesnt actually delete the file and to understand why we need to take a closer look at how these operating systems handle storage and access to files so when you have a mechanical hard drive your files and folders are stored in what are called sectors of the spinning disc and each one of these sectors has enough space for about 512 bytes and windows the mac os and linux keep track of what sectors have data in them and what data is in those sectors by using pointers and a pointer works kind of like a directional sign that tells you something is located in a specific place so the pointer doesnt actually represent the file itself or the data that is in it but rather it just represents where yo
At DocHub, your data security is our priority. We follow HIPAA, SOC2, GDPR, and other standards, so you can work on your documents with confidence.
Learn more



