
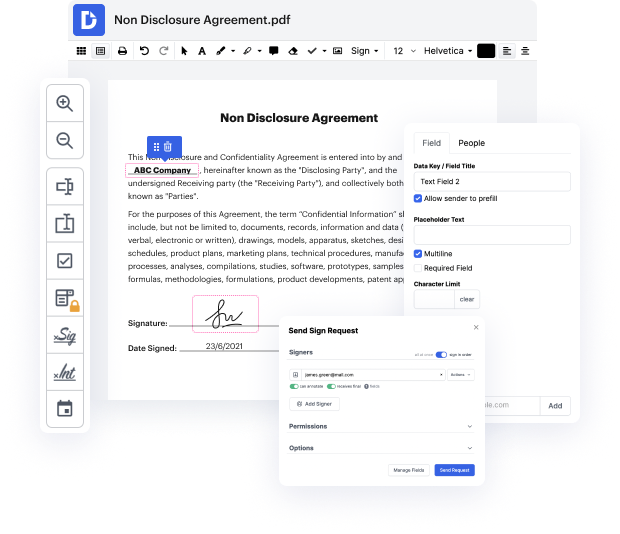
Editing xml is fast and straightforward using DocHub. Skip downloading software to your PC and make changes with our drag and drop document editor in just a few easy steps. DocHub is more than just a PDF editor. Users praise it for its ease of use and powerful features that you can use on desktop and mobile devices. You can annotate documents, create fillable forms, use eSignatures, and send documents for completion to other people. All of this, put together with a competing price, makes DocHub the ideal decision to conceal texture in xml files effortlessly.
Make your next tasks even easier by converting your documents into reusable templates. Don't worry about the protection of your records, as we securely store them in the DocHub cloud.
pretty short bit segment I explained what application context is in this tutorial Iamp;#39;ll be explaining the difference between Android and app in XML you can see in my activity main.xml file I have the tag Android and I also have this tag over here for app in my text view now Android is used for attributes coming directly from the Android SDK itself her as app is often used if we were using a support library which in this case you can see is constraint via a bulldog Gradle file indeed I do have implementation Android extra constraint male and that is something that Iamp;#39;m adding to my build up Gradle file as a dependency and that is why over here and and my constraint layout after pride the app tag because this is something that Iamp;#39;m using from an external support library whereas Android is and is a attribute that comes from the Android SDK the app namespace is also used for custom defined attributes which can be made in attrs to xml which is a type of file that you ca