
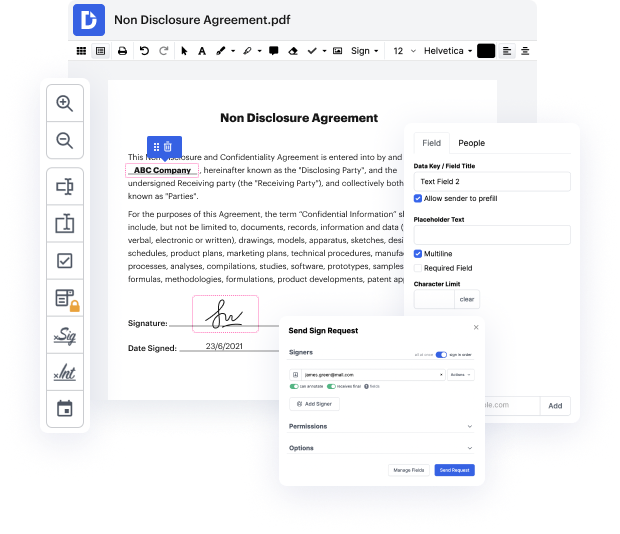
No matter how complex and challenging to modify your documents are, DocHub offers a simple way to change them. You can change any part in your HWP without extra resources. Whether you need to tweak a single component or the entire form, you can rely on our powerful solution for quick and quality outcomes.
Additionally, it makes certain that the final form is always ready to use so that you can get on with your tasks without any delays. Our extensive collection of features also includes advanced productivity tools and a catalog of templates, allowing you to make the most of your workflows without the need of wasting time on repetitive operations. On top of that, you can gain access to your papers from any device and incorporate DocHub with other solutions.
DocHub can handle any of your form management operations. With an abundance of features, you can generate and export documents however you want. Everything you export to DocHub’s editor will be saved safely for as long as you need, with rigid security and data safety frameworks in place.
Check DocHub today and make handling your paperwork more seamless!
hey hereamp;#39;s a video I am docHubly overdue on making which molecule said the higher vapor pressure given two or three choices well the answer is that the higher vapor pressure will go to the molecule with the weaker intermolecular forces if you consider a liquid what youamp;#39;re measuring with vapor pressure is how easy it is for molecules to escape to the gas phase molecules that have weaker intermolecular forces feel less stuck to the other molecules and thus escape easier increasing the pressure in the gas phase so higher vapor pressure goes to weaker intermolecular forces remember hydrogen bonding and ion dipole forces are the strongest of these dipole-dipole is kind of a middle strength intermolecular force and London dispersion forces those ones that come up when thereamp;#39;s no polarity or hydrogen bonding are the weakest so letamp;#39;s do some alright this is just me explaining what I explained here stronger intermolecular forces mean the molecules stick toge