

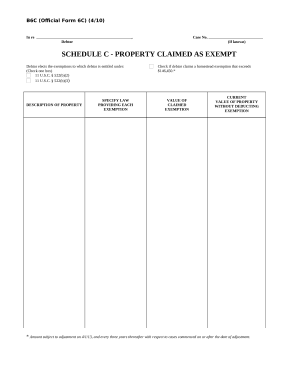

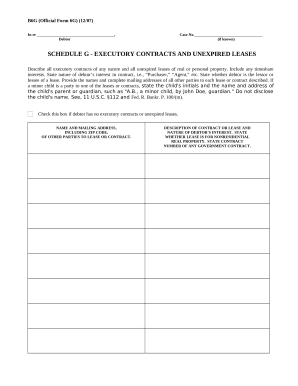
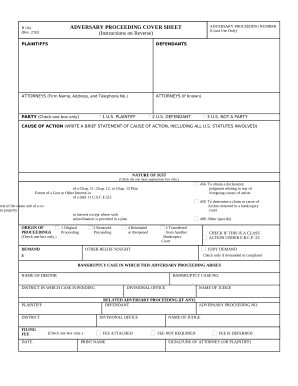



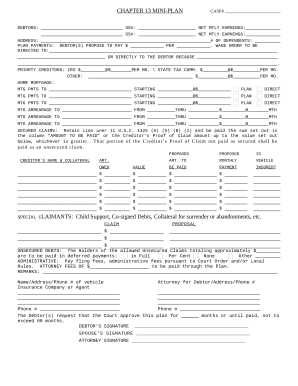























Speed up your document management with our Bankruptcy Legal Forms library with ready-made document templates that meet your needs. Access your form template, edit it, complete it, and share it with your contributors without breaking a sweat. Begin working more effectively with your documents.
How to use our Bankruptcy Legal Forms:
Explore all the possibilities for your online file administration with the Bankruptcy Legal Forms. Get a totally free DocHub account right now!