
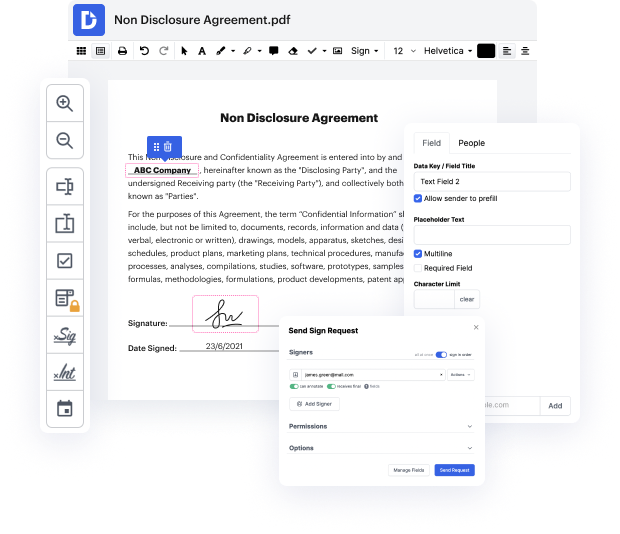
Getting complete control of your papers at any moment is important to ease your everyday duties and boost your efficiency. Achieve any objective with DocHub tools for document management and convenient PDF editing. Gain access, modify and save and incorporate your workflows with other protected cloud storage services.
DocHub gives you lossless editing, the possibility to work with any formatting, and securely eSign papers without looking for a third-party eSignature alternative. Make the most of the document managing solutions in one place. Check out all DocHub capabilities today with your free account.
In this 2-minute neuroscience tutorial, the topic of discussion is long-term potentiation (LTP), a process that strengthens synaptic connections between neurons through frequent activation. LTP is believed to facilitate changes in the brain that contribute to learning and memory. The primary mechanism involves the NMDA receptor, a type of glutamate receptor. In NMDA-receptor dependent LTP, glutamate release first activates the AMPA receptor. However, NMDA receptors, located nearby, are typically inactive at low glutamate levels due to a magnesium ion blocking their ion channel. Increased stimulation of AMPA receptors from frequent action potentials leads to depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron, enabling LTP.