
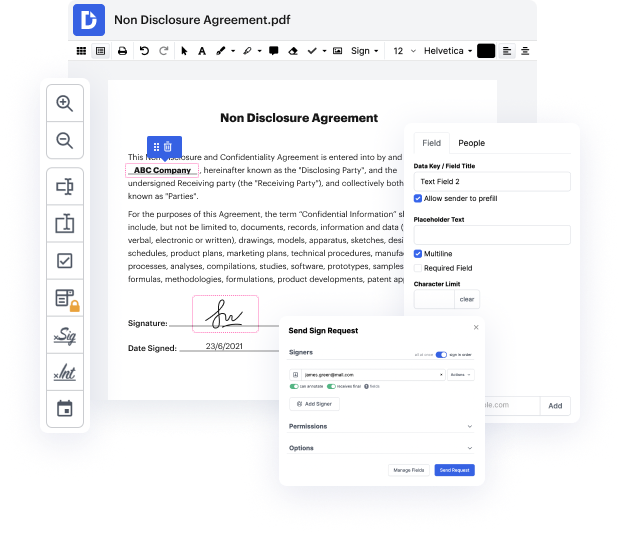
Not all formats, including zip, are created to be effortlessly edited. Even though numerous capabilities can help us edit all file formats, no one has yet created an actual all-size-fits-all solution.
DocHub offers a straightforward and efficient solution for editing, handling, and storing documents in the most widely used formats. You don't have to be a technology-knowledgeable person to bind motif in zip or make other changes. DocHub is powerful enough to make the process easy for everyone.
Our feature enables you to change and tweak documents, send data back and forth, generate dynamic forms for information gathering, encrypt and protect paperwork, and set up eSignature workflows. Moreover, you can also generate templates from documents you utilize regularly.
You’ll find plenty of other functionality inside DocHub, such as integrations that allow you to link your zip file to a wide array of productivity programs.
DocHub is an intuitive, fairly priced option to deal with documents and improve workflows. It offers a wide range of tools, from generation to editing, eSignature providers, and web document building. The software can export your files in multiple formats while maintaining maximum safety and following the maximum information safety requirements.
Give DocHub a go and see just how easy your editing operation can be.
welcome we have learned about the activators which are of the three types true activator chromatin remodeling complexes which are also called as the anterior pressures architecture proteins now the true activators are the activities which are going to bound with the DNA that is to the gene to be expressed and these activities it has a two domains one it is a DNA binding two main and the second one it is the activity region so here the DNA binding domain they are very distinct and they are very specific one as the sequence of the DNA it is going to change as the name suggests DNA binding domain these domain or these motifs they are involved into the binding to the DNA and as the DNA it is going to change the gene it is going to change the sequence it is going to change the DNA Motif or the DNA domains they are also going to vary from the activator to the activator so todayamp;#39;s topic it is the DNA binding domain the DNA binding domain it is it is of the four types okay first one it